As the world faces urgent challenges like climate change, resource depletion, and food security, one issue remains surprisingly underexamined: food waste. Beyond being an economic inefficiency, food waste is a significant environmental concern. In the era of data and technology, food waste analysis has become essential to addressing this crisis. Leveraging data-driven insights, food waste analysis provides innovative solutions to minimize waste, reduce costs, and build more sustainable food systems. This blog explores how harnessing analytical tools can revolutionize food waste management, paving the way for sustainability and operational efficiency.
Quantzig, an advanced analytics and business intelligence solution providers, offers waste management analytics dashboard to tackle the most promising challenges in the food industry. By leveraging advanced data analytics, our dashboard provides actionable insights into waste generation, enabling businesses to identify inefficiencies, optimize production processes, and reduce costs.
Book a demo to experience the meaningful insights we derive from data through our waste management analytical tools and platform capabilities. Schedule a demo today!
Request a demoTable of Contents
Challenges in waste management data collection
Waste Monitoring:
Continuous monitoring of waste generation and disposal plays a crucial role in zero waste analytics, offering insights into the scale of food waste within an organization. By leveraging data-driven approaches, businesses can identify inefficiencies and establish a foundation for meaningful improvements. Implementing regular audits and tracking systems ensures organizations remain proactive in their waste management strategies, driving sustainability and operational efficiency.
Environmental Responsibility:
Food waste analysis plays a crucial role in reducing waste and mitigating the environmental impact of global food systems. By leveraging data-driven insights, businesses can identify inefficiencies and implement sustainable practices such as recycling, composting, and resource reuse. These strategies not only contribute to global sustainability goals but also enhance an organization’s corporate social responsibility, fostering a more eco-conscious and efficient food system.
Cost Efficiency:
Reducing food waste is not just about being environmentally responsible; it’s also a matter of bottom-line savings. By streamlining operations, managing inventory more effectively, and reducing excess production, businesses can cut down on waste-related expenses. These savings can be reinvested into other areas of the organization for growth.
Indoor Facility Management:
Proper management of storage conditions and inventory tracking plays a critical role in minimizing food waste. Ensuring that food is stored at the right temperature and that stock is rotated properly can reduce spoilage and waste. An efficient distribution process ensures that excess food is directed to the right channels rather than being discarded.
Waste Stream Identification:
To reduce waste, businesses must first understand the different types of waste they generate. Identifying the sources of waste—whether it’s from overproduction, spoilage, or consumer behavior—helps in targeting the root causes. With this insight, organizations can develop tailored strategies to cut down on waste at every stage of the process.
Leveraging Big Data & AI:
Big Data and AI technologies offer powerful tools for predicting waste generation and optimizing management strategies. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, organizations can make data-driven decisions to prevent waste before it occurs. These technologies also allow for real-time monitoring and adjustment, ensuring that food waste is minimized continuously.
Medical Waste Handling:
Special care must be taken with medical waste, as it presents unique challenges and risks. Proper disposal, in line with regulations, is critical to prevent harm to the environment and human health. Collaboration with regulatory bodies ensures that businesses follow the appropriate procedures for safe medical waste disposal and compliance with local laws.
Comprehensive Waste Management Framework:
A comprehensive approach to waste management involves collecting and analyzing data across the entire lifecycle—from generation to disposal. By assessing each stage, businesses can identify inefficiencies, improve resource allocation, and continuously enhance their waste management systems. This data-driven approach ensures long-term sustainability and reduces operational costs.
Collaboration with Regulators:
Effective waste management requires coordination between businesses and local regulatory bodies. By working together, organizations can ensure that their waste practices meet legal requirements and environmental standards. This collaboration also helps businesses stay informed about new regulations and emerging best practices in waste management.
Environmental Impact of Food Waste
Food waste not only has significant economic costs, but it also poses a severe threat to the environment. In fact, food waste is one of the largest contributors to global greenhouse gas emissions. This waste contributes to the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, in landfills where decomposing food cannot properly break down.
The Hidden Carbon Footprint
The carbon footprint of food waste is staggering. When food is discarded, it not only wastes the resources like water, land, and labor used to produce it but also releases carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane into the atmosphere, further exacerbating climate change.
Waste Not, Want Not: The Environmental Benefits of Reducing Food Waste
By managing food waste effectively, businesses and individuals can significantly reduce their environmental impact. Efficient food waste management practices—such as better inventory tracking, reducing spoilage through improved storage, or using food waste for composting—can mitigate the harmful effects of waste.
- For example, by utilizing data analytics to predict demand, food retailers and restaurants can optimize their stock levels, reduce overproduction, and minimize waste. This not only lowers costs but helps reduce the environmental burden caused by excess food production.
- Additionally, food waste that is diverted from landfills can be repurposed in other ways. It can be composted, creating nutrient-rich soil for agriculture, or converted into renewable energy through anaerobic digestion. These practices help close the loop and contribute to a circular economy.
- The Broader Implications
- Addressing food waste goes beyond just reducing the environmental footprint. It’s a crucial element of the broader efforts to combat global hunger. Sustainable food systems are key to ensuring both food security and environmental protection.
How can Data Analytics help in food waste management?
Retailers and other businesses dealing with food products are increasingly embracing smart waste management solutions to tackle waste. These solutions utilize waste monitoring and data integration tools to analyze waste streams and identify waste patterns. By collecting and analyzing waste data, businesses can understand their waste composition and seasonal variations in demand, aiding in the formulation of waste reduction strategies. This shift from traditional waste management practices to smart waste management not only promotes cost efficiency but also supports sustainable policies and practices, ensuring the responsible use of natural resources. With user-friendly interfaces, these analytics solutions empower businesses to efficiently manage their waste and contribute to environmental challenges through effective waste reduction efforts within the food waste management strategy.
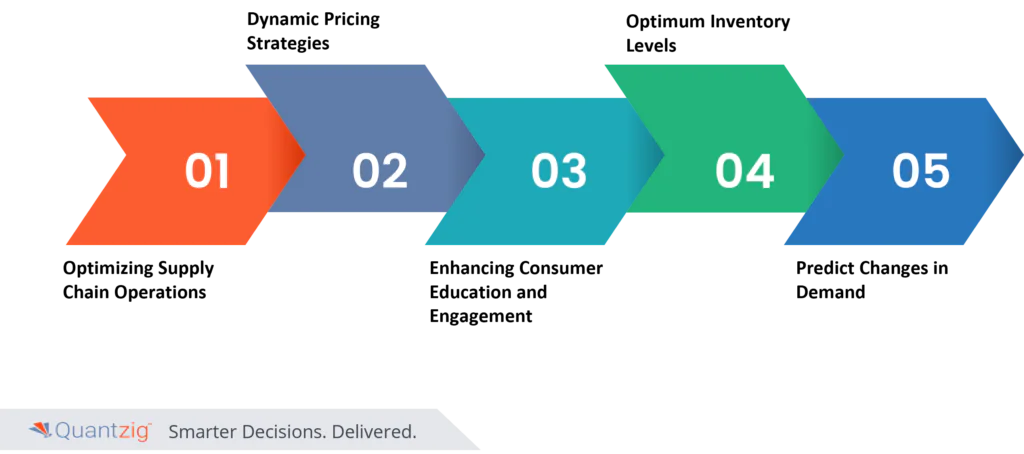
1. Optimizing Supply Chain Operations
It enables a granular analysis of the entire supply chain, offering insights into the movement of goods from production facilities to consumers. By leveraging real-time data with analytics, businesses can identify bottlenecks, reduce transit times, and optimize logistics. This streamlined supply chain not only minimizes the time perishable items spend in transit but also ensures fresher products reach the end consumer.
The integration of IoT devices and sensors in transportation vehicles allows for continuous monitoring of environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity. This ensures that perishable goods are transported and stored under optimal conditions, reducing the likelihood of spoilage.
2. Dynamic Pricing Strategies
Dynamic pricing, facilitated by analytics, proves instrumental in managing inventory nearing expiration. By adjusting prices in real-time based on factors like shelf life and current demand, businesses can incentivize consumers to purchase items before they become unsellable. This not only minimizes waste but also benefits consumers with discounted prices, creating a win-win situation.
Additionally, dynamic pricing strategies contribute to improved revenue streams, as businesses can extract value from products that might otherwise be discarded.
3. Enhancing Consumer Education and Engagement
This user-friendly tool aids businesses in comprehending consumer behavior and preferences. Through data collection and analysis, businesses can discern purchasing patterns, enabling them to customize marketing strategies and educational campaigns in line with consumer expectations. This encompasses advocating responsible consumption, highlighting the importance of waste reduction, efficient food processing, and furnishing consumers with the necessary information for informed decision-making.
By employing targeted educational campaigns backed by waste data and insights, businesses can heighten awareness regarding the environmental and social ramifications of waste. Engaging consumers in this dialogue and equipping them with knowledge empowers businesses to contribute to a collective endeavor aimed at waste reduction at the consumer level.
4. Optimum Inventory Levels
Sure, here’s the paragraph with all 20 terms included:
Analyzing sales information, weather forecasts, and seasonal trends, help manufacturers to identify an optimum inventory level which they can then use to reduce the effects of wastage. Predictions of consumer demand during a particular time can then be made and promotional plans and sales approaches can be structured around sell-by and expiry dates. This is primarily intended to cut down wastage and the knock-on environmental and cost issues that arise.
5. Predict Changes in Demand
This smart waste management solution can be utilized to identify seasonal changes in consumer demand for products. This helps retailers or restaurant chains to plan what quantity of a particular food item must be produced or procured, consequently leading to reduced waste and better management. This solution also facilitates retailers in determining the products that are closer to expiry and aggressively reducing the prices on such items so that they are consumed before their expiry date and not wasted. By employing data collection and integration, businesses can implement waste reduction strategies effectively, promoting cost efficiency and supporting sustainable practices.
Quantzig’s cutting-edge big data analytics solutions are revolutionizing the food industry landscape. Leveraging advanced data analytics techniques, our platform provides unparalleled insights into various facets of the food industry, from food processing and safety to supply chain management and consumer behavior. By harnessing the power of big data, we enable food industry stakeholders to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and drive innovation.
Experience the advantages firsthand by testing a customized complimentary pilot designed to address your specific requirements. Pilot studies are non-committal in nature.
Request a no-cost pilot
The Importance of Waste Management Analytics
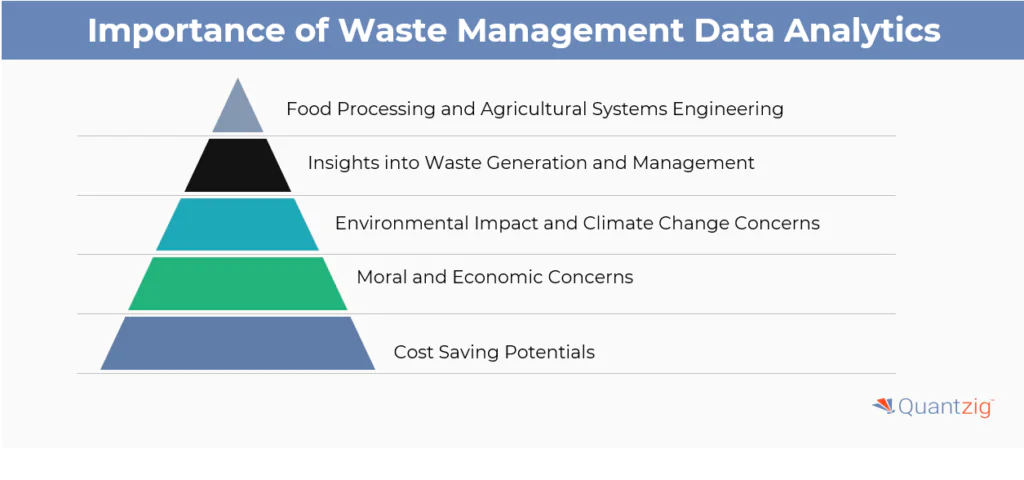
- Food Processing and Agriculture Systems Engineering: The importance of waste analytics cannot be overstated, particularly within the landscape of food processing, agriculture, and biological systems engineering, where it serves as a critical tool in addressing the global food waste problem. Waste analytics intersects with crucial concerns surrounding food safety, human consumption, and the moral and economic implications of environmental crises. It plays a pivotal role in tackling climate change concerns, notably methane emissions and water resources depletion, underscoring its significance in driving sustainable solutions.
- Insights into Waste Generation and Management: Waste analytics offers invaluable insights into waste generation and management, harnessing data to uncover patterns, identify trends, and inform data-driven decisions. By collecting and evaluating data on waste generation, disposal methods, and associated costs, organizations can optimize waste management practices and minimize environmental impacts.
- Environmental Impact and Climate Change Concerns: Efficient food processing practices facilitated by waste analytics not only ensure optimal resource utilization but also mitigate environmental impacts such as greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, proper food safety measures in waste management safeguard public health and consumer trust, while sustainable waste management solutions designed by agriculture and biological systems engineers enhance resource conservation and agricultural efficiency.
- Food Safety, Human Consumption, and Moral and Economic Concerns: Mindful human consumption habits reduce waste, aligning with moral concerns of resource stewardship and equitable distribution. Environmental issues such as greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion are mitigated through effective waste management strategies, preserving ecosystems. Economically, reducing food waste minimizes costs and fosters economic growth. Addressing the global food waste problem requires concerted efforts from all sectors to prioritize waste reduction and resource efficiency for a sustainable future.
- Cost-saving Potentials and Utilization of Waste Analytics Software: Moreover, Waste Analytics offers cost-saving potentials by optimizing waste management efforts. Utilizing Waste Analytics software, organizations can analyze data to derive insights into waste management, thus empowering them to make informed decisions and drive impactful waste management strategies.
Application of Big Data in Waste management analytics
Utilizing big data in food waste management represents a significant stride towards addressing environmental challenges and fostering sustainable policies within the food industry. This innovative approach transcends traditional waste management practices by leveraging smart waste management solutions and waste monitoring techniques. By harnessing the power of data collection and integration, businesses gain valuable insights into waste streams, waste patterns, and waste data, enabling them to formulate effective waste reduction strategies. Such initiatives not only enhance cost efficiency but also promote the responsible utilization of natural resources. Through the adoption of user-friendly interfaces and adherence to waste management policies, organizations can optimize their sustainable practices and contribute to a collective effort aimed at mitigating food waste and its detrimental impact on the environment.

1. Artificial Intelligence Systems
An awareness of big data can open doors and create a need for more sophisticated technology in the waste management space. A crucial step in this process is recycling. It can offer information on the nature, quantity, and precise locations of waste that is available.
This can assist in the use of AI-based systems to separate recyclables, as recycling is a labor-intensive procedure that carries a significant risk of disease and harm to humans. These AI-powered robots that were designed to identify and separate specific types of waste have the potential to revolutionize the recycling sector by facilitating a quicker, safer, and more affordable procedure.
2. Vehicle Recycling
The more people are being asked to use public transport the more they are inclined to buy their own cars, ironically. Considering the limit of the older cars on the roads and the average lifespan of a car, some get out of the operation for other reasons like disaster and other such conditions. This one question takes up the mind of what is feasible to do with the old and unused obsolete vehicles. It can help in understanding the location and quantity of car abandonment. This enables such businesses to get the maximum payout and also reduces the heap of probable dump.
3. Improved Inventories
It can assist in improving inventories by clarifying the quantity of a product required in each business, preventing the production or purchase of extra inventory that would otherwise be misused. Certain sectors stockpile excess during times of crisis that is never utilized; big data analytics, however, can assist in estimating the necessary quantity in advance to a certain extent.
For instance, in the pharmaceutical industry, medicine stock expires, and patient care cannot be universal. In these situations, the many items and medications that are kept on hand are wasted.
In the same way as buying too much of a middleman wastes money. In these situations, data can be gathered by big data to reduce the waste and maximize management.
Get started with your complimentary trial today and delve into our platform without any obligations. Explore our wide range of customized, consumption driven analytical solutions services built across the analytical maturity levels.
Start your trial todayAn Example: Waste management data analytics
One prominent British multinational retailer has showcased a remarkable success story in leveraging waste management data analytics for effective management. Operating on a colossal scale with approximately 110 million pounds of food products ordered daily, the organization faced the challenge of optimizing its supply chain to minimize food wastage. In response, the company adopted an informed approach, utilizing advanced analytics to enhance its inventory management and reduce instances of food waste across its numerous store locations.
Their data analytics systems harness extensive datasets from its diverse store network, employing them to develop, train, and test sophisticated algorithms. A key component of their strategy involves integrating weather forecasts into their predictive models. By analyzing weather patterns, that company enhances the accuracy of predicting shifts in food demand and food safety. While seasonal changes in consumer preferences are evident, valuable insights precisely quantify these changes, allowing for strategic inventory planning.
In essence, the success story exemplifies the power of waste management data analytics in addressing complex challenges like waste management on a large scale. Through a strategic and insightful approach, the organization has not only enhanced its supply chain efficiency but has also set a noteworthy example for the industry by demonstrating how advanced analytics can be a transformative force in achieving both environmental and economic sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of data analytics into food waste management presents a compelling zero-waste solution for B2B businesses. By leveraging insights gleaned from data analysis, businesses can streamline operations, minimize waste generation, and optimize resource utilization. This not only aligns with sustainable policies but also enhances cost efficiency and operational performance. With an effective data-driven approach, businesses can proactively identify areas for improvement, implement targeted interventions, and contribute to a more sustainable future. Embracing data analytics in food waste management represents a strategic investment that not only mitigates environmental challenges but also drives business growth and resilience in an increasingly conscious marketplace..