The importance of business analytics cannot be overstated in today’s competitive landscape, as organizations increasingly rely on data-driven insights to drive growth and achieve market excellence. No longer must business leaders depend solely on experience or intuition to make critical decisions business analytics equips them with powerful tools to analyze market dynamics, optimize productivity, and assess financial performance with precision. By leveraging extensive research and advanced quantitative methods, enterprises can uncover valuable trends, patterns, and historical data, enabling strategic decision-making that fosters innovation and long-term success.
In this article, we examine the fundamentals of business analytics, examine some of its essential elements, and above all talk about why it has evolved into a vital tool for succeeding in the contemporary economy.
Book a demo to experience the meaningful insights we derive from data through our travel analytics tools and platform capabilities. Schedule a demo today!
Request a Free DemoTable of Contents
What is Business Analytics Definition?
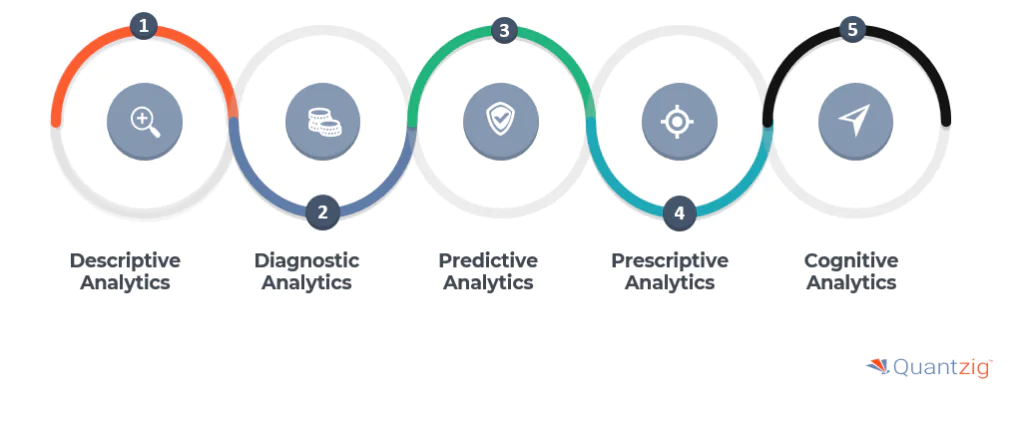
Business analytics refers to the practice of using statistical methods, data analysis, and technologies to examine and interpret business data. The goal is to identify patterns, trends, and insights that can help organizations make informed, data-driven decisions, improve performance, and gain a competitive advantage. Business analytics involves the use of data mining, predictive modeling, and various quantitative techniques to solve business problems and optimize operations. It can be categorized into descriptive, diagnostic predictive, prescriptive and cognitive analytics, each serving different purposes in the decision-making process.
Types of Business Analytics Techniques:
The primary types of business analytics are:
- Descriptive Analytics: Focuses on summarizing and analyzing historical data to understand past trends and patterns. It answers the question, “What happened?” Common tools include dashboards, reports, and visualizations that depict historical data.
- Diagnostic Analytics: Goes deeper by interpreting data to determine why something happened. It uses techniques like data mining, correlations, and drill-downs to identify root causes behind past outcomes. The key question here is, “Why did it happen?”
- Predictive Analytics: Leverages the insights from both descriptive and diagnostic analytics to forecast future trends or behaviors. It answers the question, “What is likely to happen?” Techniques include statistical models, machine learning, and forecasting methods.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Suggests actions to take based on the analysis of historical and predicted data. It focuses on determining what should be done to achieve desired outcomes and improve decision-making. This type of analytics uses optimization models, simulation, and decision analysis.
- Cognitive Analytics: Incorporates artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to mimic human intelligence. It aims to provide deeper insights by analyzing data in a more contextual manner, uncovering hidden patterns, and making sense of complex and unstructured data. The focus is on enhancing decision-making with systems that understand, reason, and learn over time.
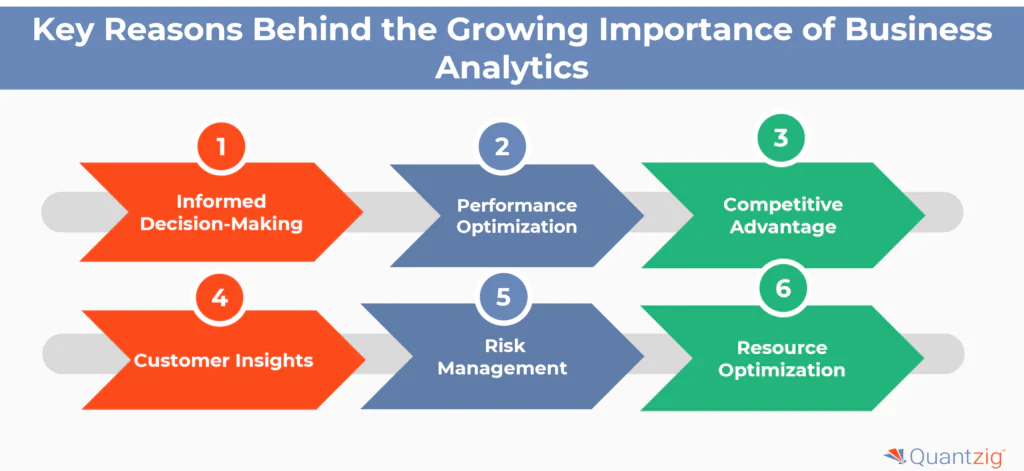
Key Reasons Behind the Growing Importance of Business Analytics:
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| 1. Data Explosion | Businesses generate vast amounts of data from sources like social media and IoT. Analytics helps extract valuable insights from this data. |
| 2. Increased Competition | Business analytics helps companies understand market trends, customer preferences, and inefficiencies, providing a competitive edge. |
| 3. Data-Driven Decision Making | Data-driven decisions reduce uncertainty, offering factual insights for better accuracy in decision-making. |
| 4. Technological Advancements | Advanced tools, cloud computing, and AI make sophisticated analytics accessible to businesses at lower costs. |
| 5. Customer Personalization | Analytics allows businesses to tailor products, services, aid to risk management and marketing strategies based on customer behavior and preferences. |
| 6. Operational Efficiency | By identifying inefficiencies, analytics helps optimize processes, increase productivity, and improve resource allocation. |
| 7. Risk Management | Predictive analytics helps businesses foresee and mitigate financial risks, supply chain disruptions, and fraud. |
| 8. Regulatory and Compliance Needs | Analytics ensures businesses adhere to legal and regulatory standards, especially in finance and healthcare sectors. |
| 9. Real-Time Decision Making | Real-time analytics enables quick responses to market shifts, customer demands, and operational changes. |
| 10. Cost Reduction | Analytics identifies cost-saving opportunities, optimizes resources, and improves financial performance. |
These factors drive the importance of business analytics, making it essential for maintaining competitiveness and growth
Experience the advantages firsthand by testing a customized complimentary pilot designed to address your specific requirements. Pilot studies are non-committal in nature.
Request a free pilotEvolution of Business Analytics
The evolution of business analytics can be traced through several distinct phases, reflecting advancements in technology, data processing, and decision-making approaches. Here’s a breakdown of its evolution:
Early Days: Manual Analysis (Pre-1970s)
Approach: Data was manually collected and analyzed using basic statistical techniques. Tools: Manual spreadsheets, basic statistics, and hand-written reports. Focus: Limited to small datasets and simple analysis, often used for accounting, finance, and operational management. Key Limitation: Lack of automation and computational power made it difficult to analyze large datasets or perform advanced analysis.
Data Warehousing and Decision Support Systems (1970s-1990s)
Approach: The rise of databases, data warehouses, and Decision Support Systems (DSS) enabled organizations to collect, store, and query large volumes of data. Tools: Relational databases, SQL, and early Business Intelligence (BI) tools. Focus: Companies began aggregating data from different sources and using it for basic reporting and descriptive analytics. Key Limitation: Data analysis was still largely backward-looking, focusing on understanding what had already happened (descriptive analytics).
Business Intelligence (1990s-2000s)
Approach: BI systems emerged, allowing companies to conduct more complex data analysis with better visualization and reporting capabilities. Tools: OLAP (Online Analytical Processing), dashboards, and data visualization tools like Crystal Reports and Microsoft BI. Focus: Increased use of data for reporting, performance tracking, and KPI monitoring. The focus was still primarily descriptive, but BI improved the accessibility of data to decision-makers. Key Limitation: Limited ability to predict future trends or provide prescriptive insights.
Predictive Analytics (2000s-2010s)
Approach: The development of more advanced statistical models, machine learning algorithms, and data mining techniques allowed businesses to shift from simply describing past events to predicting future outcomes. Tools: Predictive models, data mining tools (SAS, SPSS), and machine learning algorithms. Focus: Businesses started leveraging data to anticipate future trends, customer behaviors, and operational risks. Predictive analytics became widely used in areas like customer segmentation, demand forecasting, and fraud detection. Key Limitation: Predictive analytics gave insights into future possibilities but did not necessarily provide recommendations on how to act on these predictions.
Big Data and Advanced Analytics (2010s-2020s)
Approach: The advent of big data technologies enabled organizations to process massive, complex datasets in real-time. The rise of cloud computing and distributed computing (Hadoop, Spark) fueled this transformation. Tools: Big data platforms (Hadoop, Spark), AI, machine learning, and advanced analytics platforms like Tableau, Power BI, and Google Analytics. Focus: In addition to predictive analytics, businesses began using prescriptive analytics to recommend actions based on data insights. Organizations also started harnessing unstructured data (social media, sensors, images). Key Limitation: While powerful, big data technologies required significant expertise and infrastructure investment, and privacy concerns began to arise as data collection practices expanded.
AI and Cognitive Analytics (2020s-Present)
Approach: Artificial intelligence (AI) and cognitive analytics enable machines to simulate human thought processes, understanding, learning, and decision-making. Advanced AI-driven tools can autonomously analyze data, learn from it, and even take actions based on insights. Tools: AI, machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing (NLP), and automated analytics platforms. Focus: Emphasis is on real-time, automated decision-making and autonomous systems. Businesses can gain deeper insights from vast amounts of unstructured and structured data, and AI can recommend or implement decisions without human intervention. Key Limitation: Ethical and regulatory concerns related to data privacy, bias in AI models, and transparency in AI-driven decision-making.
Future Trends
AI-Driven Analytics: Expect further integration of AI into all aspects of business analytics, with greater emphasis on autonomous decision-making systems. Edge Analytics: As IoT devices proliferate, edge computing will allow data analysis at the source, reducing latency and enabling real-time insights in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and retail. Blockchain and Analytics: Blockchain technology may play a role in enhancing data security, transparency, and integrity in business analytics.
Reasons Why to Choose Quantzig’s Business Analytics Solutions
1. Comprehensive Expertise in Analytics:
The importance of business analytics is evident in Quantzig’s comprehensive solutions, which span the entire analytics lifecycle from data gathering and management to advanced analytics and actionable insights. With expertise in descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, Quantzig enables businesses to effectively leverage data for strategic decision-making.
Their specialization across industries such as retail, healthcare, manufacturing, financial services, and telecommunications underscores the importance of business analytics in addressing unique challenges. By delivering tailored analytics solutions, Quantzig helps organizations optimize performance, enhance decision-making, and drive sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive market.
2. Proven Track Record:
Quantzig has a proven track record of successful client engagements, having collaborated with numerous global brands to enhance business operations, improve decision-making, and drive growth through data-driven strategies. Their extensive collection of case studies and testimonials highlights how they have helped organizations overcome business challenges through advanced analytics solutions, building trust in their ability to deliver measurable and impactful results.
3. Experienced Team of Data Scientists and Analysts:
Quantzig’s team comprises highly skilled data scientists, business consultants, and analysts who excel in data-driven decision-making, leveraging their expertise across various industries to develop insights that align with business objectives. Their deep knowledge of domain ensures a strong understanding of both data and business processes, allowing them to deliver practical and relevant analytics solutions that drive strategic success.
4. Tailored, Scalable Solutions:
Quantzig offers customizable analytics, tailoring its solutions to fit the unique needs of clients across various domains, whether in customer analytics, supply chain optimization, or financial forecasting. As businesses expand and their analytics requirements evolve, Quantzig provides scalable services, ensuring organizations can continue leveraging data-driven insights without the need for extensive system overhauls, ultimately driving efficiency and sustainable growth
5. Focus on ROI and Business Impact:
Quantzig follows a results-driven approach, delivering analytics solutions that enhance profitability, operational efficiency, and market competitiveness by aligning projects with key business objectives to ensure measurable outcomes. Their focus on data-driven decisions enables organizations to leverage clear metrics and KPIs, transforming insights into actionable strategies that improve decision-making and maximize the value extracted from data.
6. Cross-Industry Solutions:
Quantzig’s analytics solutions are not limited to a specific industry but span across retail, manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and more. This cross-industry experience helps them transfer best practices and innovative solutions from one sector to another.
Get started with your complimentary trial today and delve into our platform without any obligations. Explore our wide range of customized, consumption driven analytical solutions services built across the analytical maturity levels.
Start your free trial now
Conclusion
The importance of business analytics in today’s competitive landscape cannot be overstated, as organizations increasingly rely on data-driven strategies to thrive. By leveraging business intelligence analytics and advanced analytics tools, companies can extract valuable insights that enhance decision-making and operational efficiency. Investing in a robust business analytics platform and utilizing enterprise business analytics solutions allows businesses to optimize processes and maintain a competitive edge. Additionally, business analytics consulting helps organizations select the most suitable and affordable analytics solutions, including cloud-based and custom software development, ensuring scalability and efficiency. A strong focus on data-driven business analytics for marketing, combined with advanced predictive analytics, empowers companies to improve performance and achieve long-term success
Related Case Study
AI Pricing Analytics: Revolutionizing Business Strategies
- Author: Associate Vice President, Analytics and Data Strategy, Quantzig. Introduction to AI ...